Array advanced
- Array basic
- Array advancedYou are here
Squares of a Sorted Arrays
Given an integer array
numssorted in non-decreasing order, return an array of the squares of each number sorted in non-decreasing order.
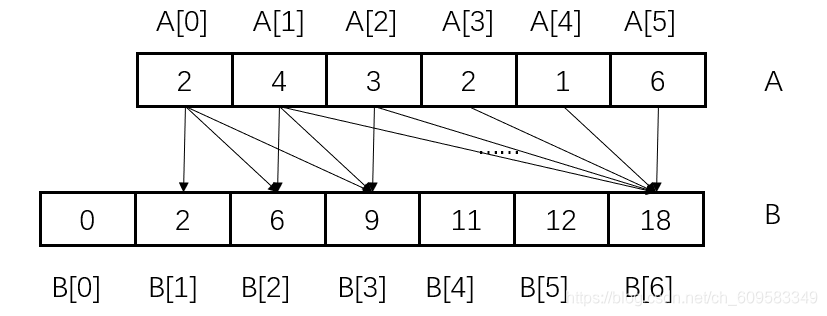
The ordinary method is to square each number in the array and sort the array; in this situation, the time complexity is O(n+nlogn).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
nums[i]=nums[i]*nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums);//fast sort
return nums;
}
}
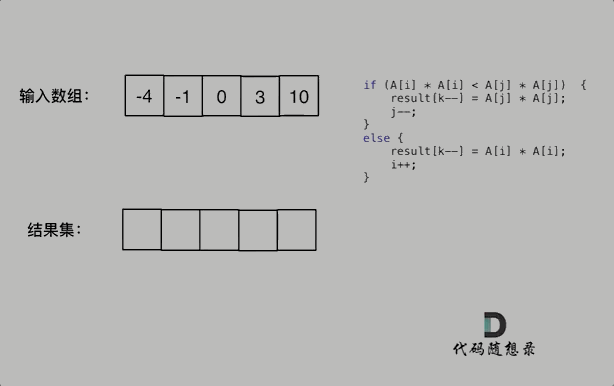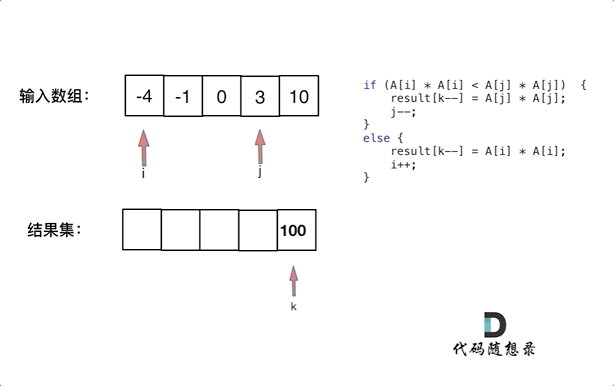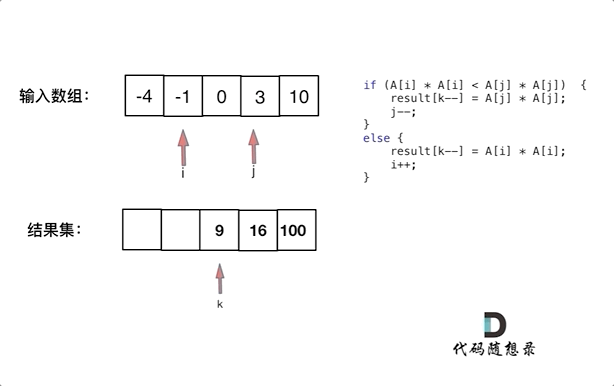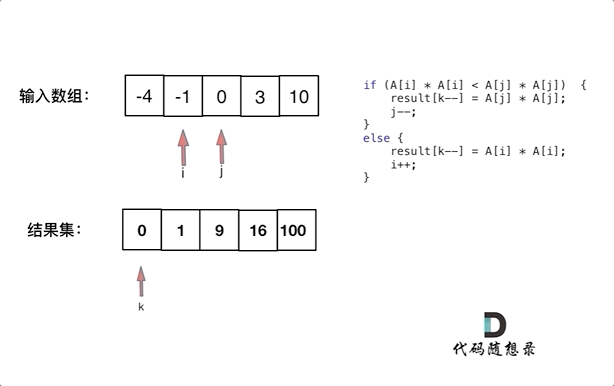
Two-point method
The given array is sorted; after the square, the negative elements square might be greater than the opposite one.
So we first square the array, then use two points, one point on the left, and one point on the right, in the loop, compare the left and right’s numbers, and put the greater one to the new int[] (in the new array, the point is at the end)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length-1;
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
for(int j =right;j>=0;j--){
if(nums[left]*nums[left]>nums[right]*nums[right]){
result[j]=nums[left]*nums[left];
left++;
}else{
result[j]=nums[right]*nums[right];
right--;
}
}
return result;
}
}
Minimum Size Subarray Sum
Question:
Given an array of positive integers
numsand a positive integertarget, return the minimal length of a subarray whose sum is greater than or equal to thetarget. If there is no such subarray, return0instead.
There are three solutions:
- For the force solution, use two for the loop; I don’t recommend it.
- Prefix solution: since the provided array is asked for the subarray and the subarray’s sum, we can use the prefix method to solve this question.
About prefix:
1
2
3
4
5
prefixSum[0] = a[0]
prefixSum[1] = a[0] + a[1]
prefixSum[2] = a[0] + a[1] + a[2]
...
prefixSum[i] = a[0] + a[1] + ... + a[i]
So, we can simply use the following loop to get a prefix array:
1
2
3
4
5
6
const n = nums.length
const sum = [0]
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + nums[i - 1]
}
Back to this problem: after getting the prefix array, we can use two points to select the minimal length subarray (greater than the target).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int[] prefix = new int[nums.length+1];
for(int i = 1;i < prefix.length;i++){
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + nums[i-1];
}
int left = 0;
int right = 1;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while(left != right && right < prefix.length){
if(prefix[right] - prefix[left] < target){
right++;
}else{
min = Math.min(min,right-left);
left++;
}
}
return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE?0:min;
}
}
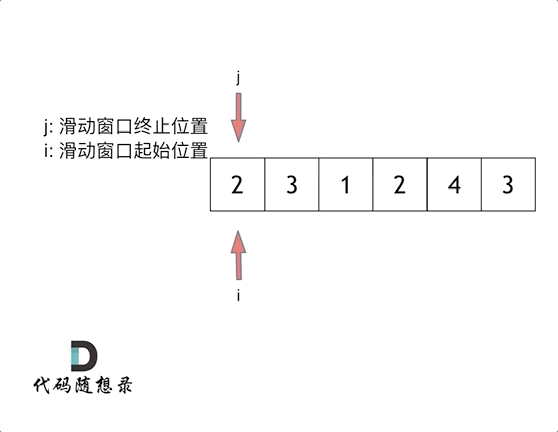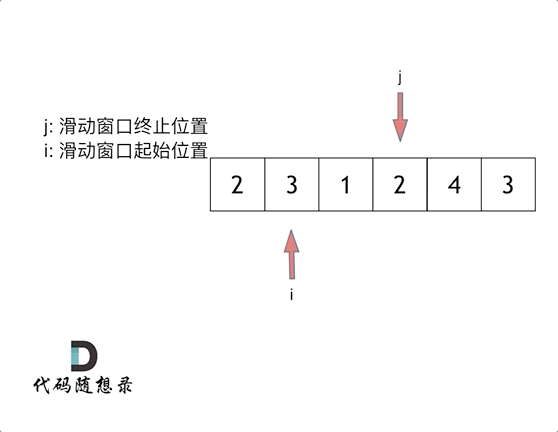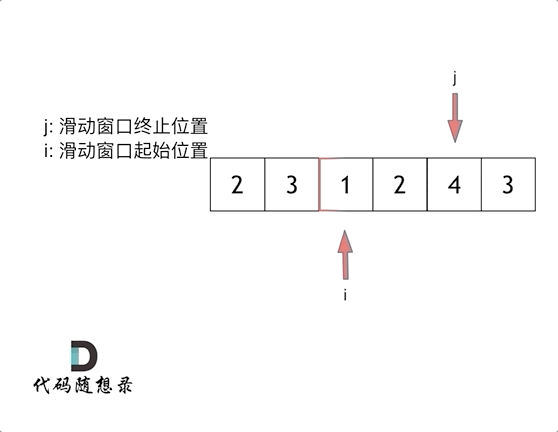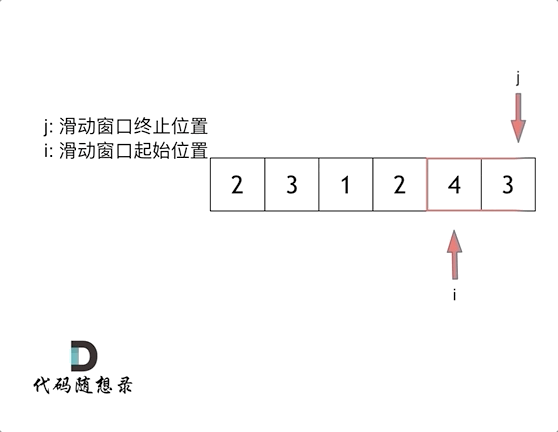
- Sliding window:
What does sliding window mean?
A sliding window is a process that constantly adjusts the start and end positions of the subsequence and eventually gets our needed outcomes.
In the force solution, we use two for loops to describe this constant search interval process, but how do we use one for loop to complete this function?
Three points need to be discussed:
- Is the start or end position the indexing of the for loop?
End position.
- What is the window inside the sliding window?
The window is a subarray (In this problem, a great window means the window’s elements sum greater than the target).
- When should the start position move?
Once the window’s elements sum greater than the target, we move the start position point to decrease the window.
So the key step in the sliding window is, according to the current window’s sum outcome, constantly changing the start point’s position, decreasing the force solution’s time complexity from O(n^2) to O(n).**
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int start = 0; // start is the start point
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int sum = 0;//define the window's elements sum
int subLength = 0;//define the subarray's length
for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){// i is the end's point location,特别注意此处for循环中存放的是window结束位置的指针
sum += nums[i];
while(sum >= target){
subLength = i-start+1;
result = result < sublength ? result : subLength;
sum -= nums[start];
start++;
}
}
return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE?0:result;
}
}
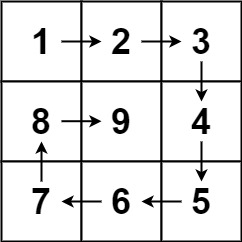
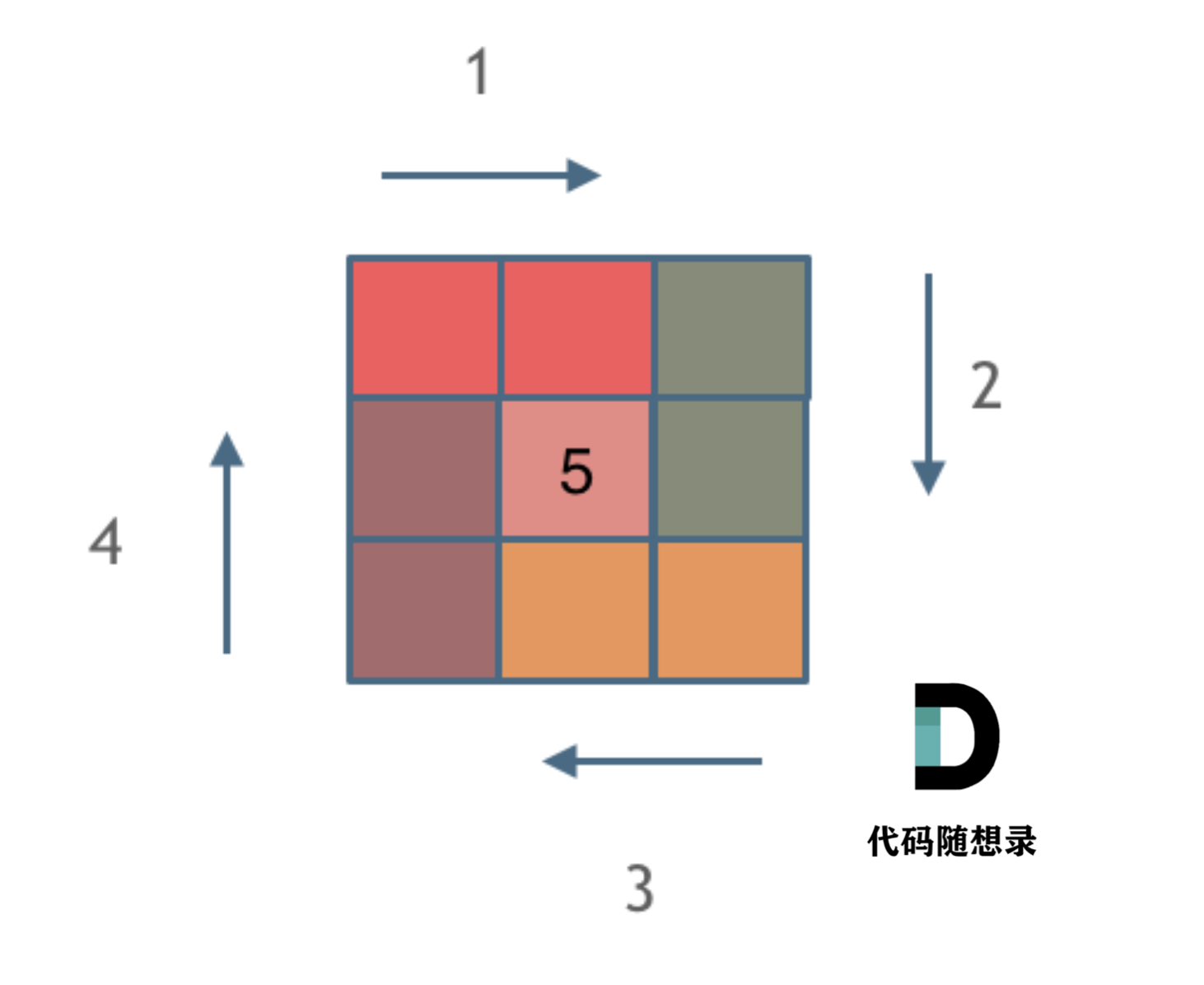
Spiral Matrix II
Given a positive integer
n, generate ann x nmatrixfilled with elements from1ton2in spiral order.Example Input and Output:
We need to consider four points in this rectangle. Are all these turn points handled by the current or next edge?
Be in mind: In each loop, we maintain the rules for handling each edge.
Here, we use the [start, end) rule, which means we deal with the start point and not process the end point.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int startX = 0;
int startY = 0;//define each while loop's begin location
int loop = n / 2;//define while loop times
int count = 1;//the value assigned to each cell in the loop
int i = 0;//i represents the line number in each loop
int j = 0;//j represents the collum number in each loop
int offset = 1;//offset is used to control the length of each edge traversal in each loop, plus 1 in each loop (plus 1 means that the right boundary of the loop is contracted by one bit).
int[][] result = new int[n][n];
while (loop-- > 0) {
i = startX;
j = startY;
//Four edges are processed in each loop, using four for loops to process them, and left-closed-right-open to process them
//upper rows
for (; j < n - offset; j++) {
result[i][j] = count;
count++;
}
//right column
for (; i < n - offset; i++) {
result[i][j] = count;
count++;
}
//lower rows
for (; j > startY; j--) {
result[i][j] = count;
count++;
}
//left column
for (; i > startX; i--) {
result[i][j] = count;
count++;
}
startY++;
startX++;
offset++;
}
//To handle the case where n is an odd number, the middle-most cell needs to be assigned a separate value
if (n % 2 != 0) {
result[n / 2][n / 2] = count++;
}
return result;
}